Innovation
-
U-M team recycles previously unrecyclable plastic
PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is one of the most-produced plastics in the U.S. and the third-highest by volume worldwide. Until recently, it had a zero percent recycling rate in the U.S. But scientists at U-M recently discovered how to chemically recycle PVC into usable material.
-
New hospital to be named for D. Dan and Betty Kahn
The D. Dan and Betty Kahn Health Care Pavilion is scheduled to open in fall 2025. The $920-million facility will include 264 private inpatient rooms, a neurosciences center, specialty cardiovascular and thoracic care services, and much more.
-
The undergrads who are battling a mysterious childhood cancer
LSA and U-M undergrads, as well as recent graduates, work in a lab at Michigan Medicine to find a cure for the always-fatal DIPG brain cancer. Undaunted by statistics, they strive to create a path to survival.
-
U-M reports record $1.71B in annual research volume
Total research volume at the University increased by 8.4% in FY ’22, fueling innovations in global health, Great Lakes water quality, firearm violence, and driverless vehicle technologies. FY ’22 also marked a record high of $973M in federally sponsored research expenditures.
-
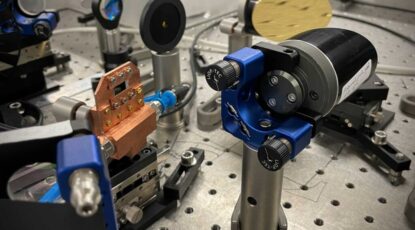
First light at the most powerful laser in the U.S.
Michigan Engineering recently fired up the Zetawatt-Equivalent Ultrashort pulse laser System, promising new developments in medicine, electronics, and national security. Funded by the National Science Foundation, ZEUS will explore the physics of the quantum universe.
-
Engineering tough: Taking the F-150 electric
As chief nameplate engineer for the F-150 Lightning, Linda Zhang, BSE EE ’96/MSE CE ’98/MBA ’11, has impacted the design, development, and delivery of the electric vehicle, as well as the creation of its new manufacturing plant and Ford’s marketing campaign.
-
U-M study: Local renewable energy employment can fully replace U.S. coal jobs nationwide
As of 2019, coal-fired electricity generation directly employed nearly 80,000 workers. A new U-M study quantifies—for the first time—the technical feasibility and costs of replacing those coal jobs with local wind and solar employment nationwide.
-
Emulating impossible ‘unipolar’ laser pulses paves the way for processing quantum information
A laser pulse that sidesteps the inherent symmetry of light waves could manipulate quantum information, potentially bringing us closer to room temperature quantum computing. The study could also accelerate conventional computing
-
21 research takeways from ’21
Pandemic-related stories may dominate the news, but these other significant findings and developments at U-M also deserve attention.